Blog
Dental hygiene tips for healthy teeth & gums
A Comprehensive Guide To Teeth
Teeth play an essential role in our daily lives, not just in our capacity to chew food but also in our overall health and beauty. This thorough guide enables individuals to prioritize their dental well-being by providing insights into teeth anatomy, effective teeth cleaning practices, and prevalent concerns.
I. Teeth Anatomy:
a. Tooth Structure: Several layers that include enamel, dentin, pulp, and cementum.
- Enamel: The most rigid substance in the body, enamel is the outermost layer and protects against degradation.
- Dentin is a sensitive layer that connects to the pulp beneath the enamel.
- The pulp comprises nerves and blood vessels that aid in tooth development and sensitivity.
- The cementum covers the tooth roots and secures the tooth to the jawbone.
b. Teeth Types:
- Incisors are the front teeth that are used for cutting.
- Canines are pointed teeth used for ripping.
- Premolars and molars are back teeth with flat tops that are used for grinding and crushing.
II. Good Oral Health Practices:
a. Use a circular motion to clean thoroughly without causing harm.
b. Floss at least once daily to eliminate plaque and food particles between teeth. Proper flossing techniques aid in the prevention of gum disease and cavities.
c. Schedule biannual dental exams for professional cleanings and early diagnosis of dental problems. Dental practitioners can address individual oral health needs through personalized recommendations.
d. Eat a well-balanced diet high in fruits and vegetables, dairy, and lean proteins. To avoid tooth decay, limit your intake of sugary snacks and acidic liquids.
e.To reduce your risk of gum disease, tooth loss, and oral cancer, stop smoking and using tobacco products.
f. Moderate alcohol consumption benefits general oral health and lowers the risk of gum disease.
g. Wear mouthguards during sports to protect your teeth from harm. Custom-fitted mouthguards provide the best protection.
III. Common Dental Issues:
a. Tooth decay: Caused by plaque buildup, tooth decay can progress to cavities and necessitates immediate treatment. Proper oral hygiene, regular check-ups, and a balanced diet are all part of prevention.
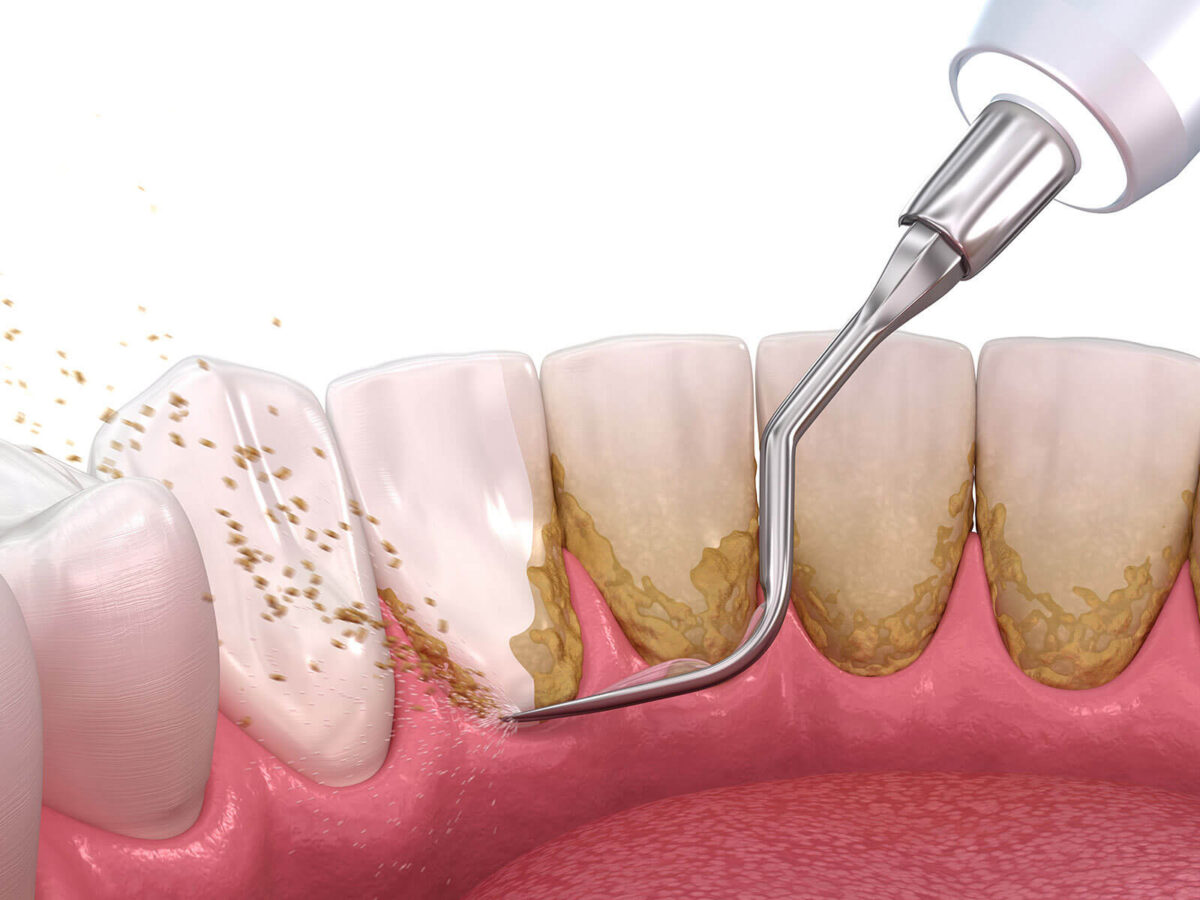
b. Gum Disease (Periodontitis): If left untreated, gingivitis, an early stage of gum disease, can proceed to periodontitis.
c. Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet triggers: Sensitivity to heat, cold, or sweet stimuli may suggest enamel degradation or exposed dentin. Sensitivity can be managed with desensitizing toothpaste and professional advice.
d. Bruxism (Tooth Grinding): Grinding or clenching your teeth can cause enamel wear, jaw pain, and migraines. Customized nightguards help safeguard your teeth while you sleep.
e. Orthodontic Problems: Malocclusion (misalignment) can result in problems such as overcrowded or crooked teeth. Orthodontic treatments, such as braces or clear aligners, aid in alignment correction.
f. Mouth Cancer: Regular dental check-ups help discover mouth cancers early. Lifestyle choices, such as abstaining from smoking and alcohol, minimize the risk.
g. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Low saliva production can be caused by drugs or certain medical disorders. Dry mouth symptoms can be relieved by staying hydrated and utilizing saliva substitutes.
IV. Specialised Dental Care:
a. Paediatric Dentistry: Early dental appointments help youngsters develop appropriate oral hygiene practices. Pediatric dentists cater to the specific dental needs of children.
b. Cosmetic Dentistry: Cosmetic procedures improve the appearance of the teeth. Popular procedures include veneers, tooth whitening, and cosmetic bonding.
c. Restorative Dentistry: Restorative procedures repair or replace lost or damaged teeth. Therapeutic options include fillings, crowns, bridges, and implants.
d. Endodontics (Root Canal Therapy): Root canal therapy treats tooth pulp infection or injury. The fundamental purpose of endodontic procedures is to preserve the natural tooth.
e. Periodontics: Periodontists treat gum problems and do gum surgery. Periodontal treatments such as scaling and root planing are popular.
Conclusion:
Prioritizing complete dental care entails understanding tooth anatomy and teeth cleaning, implementing good oral care routines, and addressing common dental issues as soon as possible. Individuals can retain healthy and brilliant smiles for the rest of their lives by incorporating basic hygiene practices, receiving regular professional dental treatment, and being aware of any risks. Remember that dental health is essential to general health; preventive treatment such as teeth cleaning adds to a confident and bright smile.
